Nour-Eddine MENAD
BRGM, France
Title: Recent Developments Of Automotive Shredder Residues Processing
Biography
Biography: Nour-Eddine MENAD
Abstract
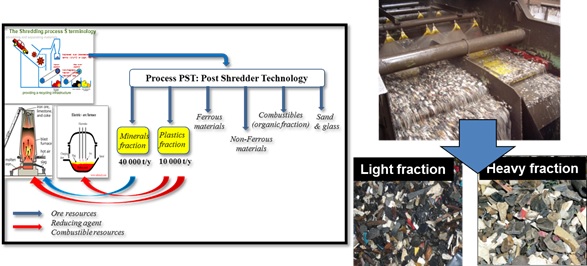
Automotive Shredder Residues (ASR) is a by-product generated during the shredding of End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) hulks, and further refined in Post-Shredder lines of Treatment (PST). European legislations impose 95% of recycling rate of ELV with 10% of energy recovery. Current recycling rate of ASR requires development of innovative processing for treating certain fractions generated from PST which are landfilled. The use of plastics-rich streams as combustible and/or alternative reducing agent in metallurgical furnaces is an industrial challenge. The whole objective of the presented work is therefore to assess the possibility of using the fractions rich in plastics in metallurgical furnaces as reducing agents. This would provide cast-iron manufacturers with chemical agents cheaper than coke. As additional potential benefits, the amount of CO2 generated in the processes and the volume of landfilled shredding residues would be lowered. This paper describes the results of chemical and mineralogical characteristics of plastics contained in ASR using multi-technical tools. Thereafter, the results of sink-float processing for the selective separation of plastics are given. The process consists in screening and developing sink-float separation techniques. About 2 tons of plastics were sieved to 4 mm. The fraction less than 4 mm representing 2.5 wt% of the total weight are eliminated. These products are essentially fluff, wood etc... The fraction higher than 4 mm representing about 712 kg are treated by the sink-float separation technique in a dense media prepared with barite (BaSO4) having a density of 1.34. The products obtained (floating and sinking) are dried, weighed and analysed. The results show that the floated fraction is well purified (it contains less than 0.5% Cl2) and can be used in metallurgical furnaces. This investigation is a good example demonstrating the efficiency of the mineral processing techniques for wastes separation and recycling.