
Youn-Woo Lee
Seoul National University, South Korea
Title: Recycling of valuable metal during supercritical water oxidation
Biography
Biography: Youn-Woo Lee
Abstract
Supercritical water oxidation (SCWO) process appears to be a viable and effective technique for recovering metals and the destruction of hazardous organics in industrial chemical process wastewater. It is demonstrated that the integration of SWS and SCWO create synergetic effect. Wastewaters from Cu-plating process, acrylonitrile manufacturing plant, liquid crystal display (LCD) manufacturing plant, and terephthalic acid (TPA) manufacturing plant were treated by SCWO not only to decompose hazardous organic compounds but also to recover valuable inorganic materials. A SCWO process was developed for treating wastewater from TPA manufacturing process which contains many organic acids such as 4-carboxybenzyl aldehyde, terephthalic acid, benzaldehyde, benzoic acid, p-tolualdehyde and p-toluic acid and inorganic compound such as cobalt and manganese acetate. During the supercritical water oxidation of organic acids, nano-particles of cobalt manganese oxide in situ formed in the reactor act as an oxidation catalyst to enhance the oxidation rate of organic acid so that one can either reduce reaction temperature or shorten residence time (Figure 1). Total organic carbon of wastewater was 37,480 ppm and was reduced to 200 ppm after reaction. Co-Mn catalyst in the TPA wastewater was recovered above 99% as cobalt manganese oxide and the size of Co-Mn oxide particles was ca. 260 nm. Figure 2 shows the commercial plant for treating TPA waste residue slurry by SCWO.
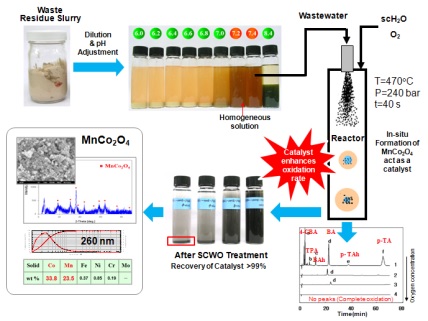
Figure 1: Schematic process flow for treating TPA waste by SCWO as well as recovery of catalysts

Figure 2: TPA waste residue slurry treatment plant by SCWO

