Day 3 :
Keynote Forum
Semiat R
Israel Institute of Technology, Israel
Keynote: Water treatments needs and directions
Time : 000

Biography:
Raphael Semiat is a professor in the Chemical Engineering Department, Technion, Haifa, Israel. He holds the Yitzhak Rabin Memorial Chair in Science, engineering and management, served as the director of the Grand Water research Institute and is in charge of the Rabin Desalination Laboratory. B.Sc. degree in Chemical Engineering from the Technion in 1973 and D.Sc. dissertation on MED Desalination in 1978 at the Technion. Expert in separation processes with industrial experience. He joined the Chemical Engineering Department, Technion, in 1990. His main research interests are: Process Development; Separation Processes with emphasis on Desalination. Of particular relevance are the research subjects associated with membranes processes and membrane fouling prevention. Most of his current research subjects are associated with the industry.
Abstract:
The challenges in water management are among the most important problems facing the world today. The shortage of clean water is at the heart of critical health issues in developing countries and is the focus of ecological and safety concerns even for the highly developed nations. To adequately provide water for drinking and agriculture, we must desalinate and clean natural water sources, reclaim polluted water, purify water with different degrees of contaminants and improve the effectiveness of water handling (storage and delivery) systems ranging from desalination plants to waste water treatment facilities and to home water purification systems. We must remove contaminants that include inorganics (metals and ions), organics (e.g. toxic waste, pharmaceuticals) and microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, etc.). At the heart of these diverse problems stands the need for new ways to clean water, to safely dispose of the extracted waste, to properly reuse the cleaning systems and to keep the environment clean. Israel made significant steps to provide affordable solutions, based on wide distribution system, desalination (close to 80% of the urban water consumption), Tertiary treatment of wastewater for irrigation, drip irrigation for reduction of water consumption and improved agriculture techniques. However, there is always place for improvements. The directions may include improved membranes, improved desalination steps in order to reduce the cost, improve pretreatment processes, increased recoveries (near zero liquid discharge in brackish water desalination), increase product quality, improved wastewater treatment by better techniques like MBR and MBBR, better treatment for removal of tracers of organic contaminants, treatment of polluted aquifers, develop small water treatment and recovery for remote locations, reduce water losses on the piping systems and more.
Keynote Forum
Nour-Eddine MENAD
BRGM, France
Keynote: Recent Developments Of Automotive Shredder Residues Processing
Time : 08:00-08:30

Biography:
Nour-Eddine Menad has completed his PhD from National School of geology of Nancy (France) and worked as Associate Professor at Technical University of Lulea (Sweden). He is scientific expert on process development on recycling of industrial wastes. He has published more than 100 papers in reputed journals and conferences, 4 patents and is in the board committee of Edorium Journal of Waste Management. At the moment, he is working at BRGM (Bureau de recherché Géologique et minière) on development of separation techniques applied on the urban mine to recover stratégic metals.
Abstract:
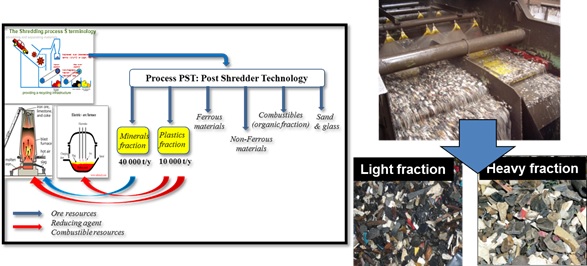
Automotive Shredder Residues (ASR) is a by-product generated during the shredding of End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) hulks, and further refined in Post-Shredder lines of Treatment (PST). European legislations impose 95% of recycling rate of ELV with 10% of energy recovery. Current recycling rate of ASR requires development of innovative processing for treating certain fractions generated from PST which are landfilled. The use of plastics-rich streams as combustible and/or alternative reducing agent in metallurgical furnaces is an industrial challenge. The whole objective of the presented work is therefore to assess the possibility of using the fractions rich in plastics in metallurgical furnaces as reducing agents. This would provide cast-iron manufacturers with chemical agents cheaper than coke. As additional potential benefits, the amount of CO2 generated in the processes and the volume of landfilled shredding residues would be lowered. This paper describes the results of chemical and mineralogical characteristics of plastics contained in ASR using multi-technical tools. Thereafter, the results of sink-float processing for the selective separation of plastics are given. The process consists in screening and developing sink-float separation techniques. About 2 tons of plastics were sieved to 4 mm. The fraction less than 4 mm representing 2.5 wt% of the total weight are eliminated. These products are essentially fluff, wood etc... The fraction higher than 4 mm representing about 712 kg are treated by the sink-float separation technique in a dense media prepared with barite (BaSO4) having a density of 1.34. The products obtained (floating and sinking) are dried, weighed and analysed. The results show that the floated fraction is well purified (it contains less than 0.5% Cl2) and can be used in metallurgical furnaces. This investigation is a good example demonstrating the efficiency of the mineral processing techniques for wastes separation and recycling.
- Networking Lunch 12:30-13:30 @ Hotel Restaurant
